1. Pelican Nebula (IC 5070)
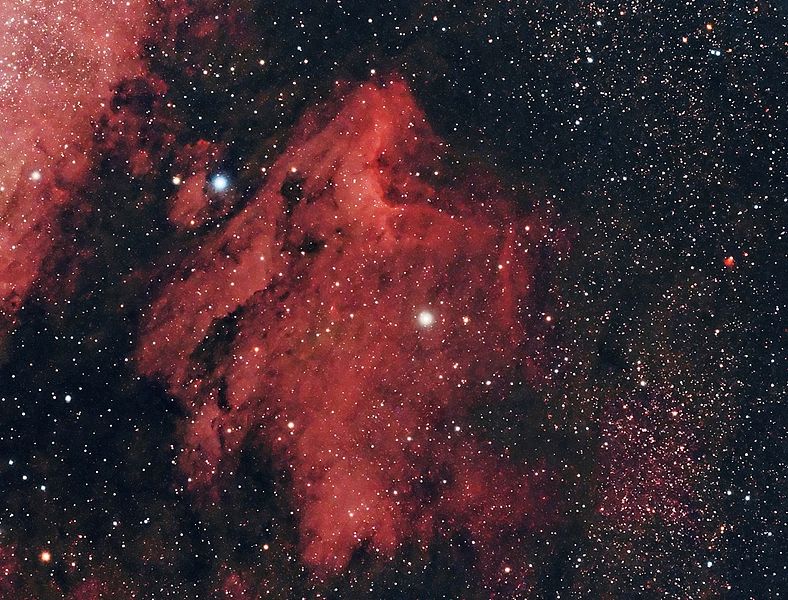

The Pelican Nebula, designated as IC 5070, is a vast cloud of interstellar gas and dust located in the constellation Cygnus (the Swan, so two birds among themselves). This emission nebula spans about 10 light-years and is illuminated by the intense radiation of nearby young, hot stars. An emission nebula refers to nebulae where the hydrogen gas itself is actually emitting light. The opposite: reflection nebulae, where the gas reflects light from young stars.
2. Butterfly Nebula (NGC 6302)
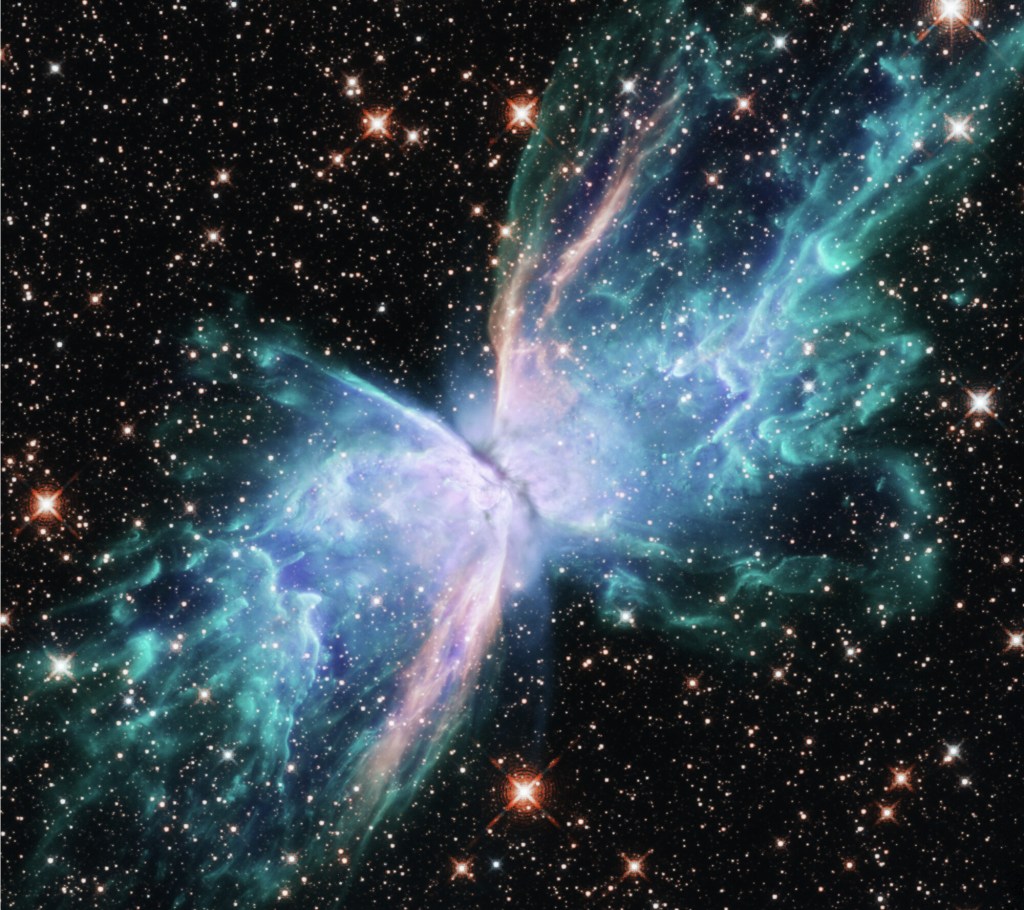

The Butterfly Nebula, also known as NGC 6302, is an example of a bipolar planetary nebula located in the constellation Scorpius. A bipolar nebula means there are two lobes on either side of a central star. Its distinctive shape, resembling the delicate wings of a butterfly, is created by the ejection of material from a dying star at its center. The star HD 155520 is a white dwarf with an estimated mass of about 0.64 solar masses.
3. Owl Nebula (M97)
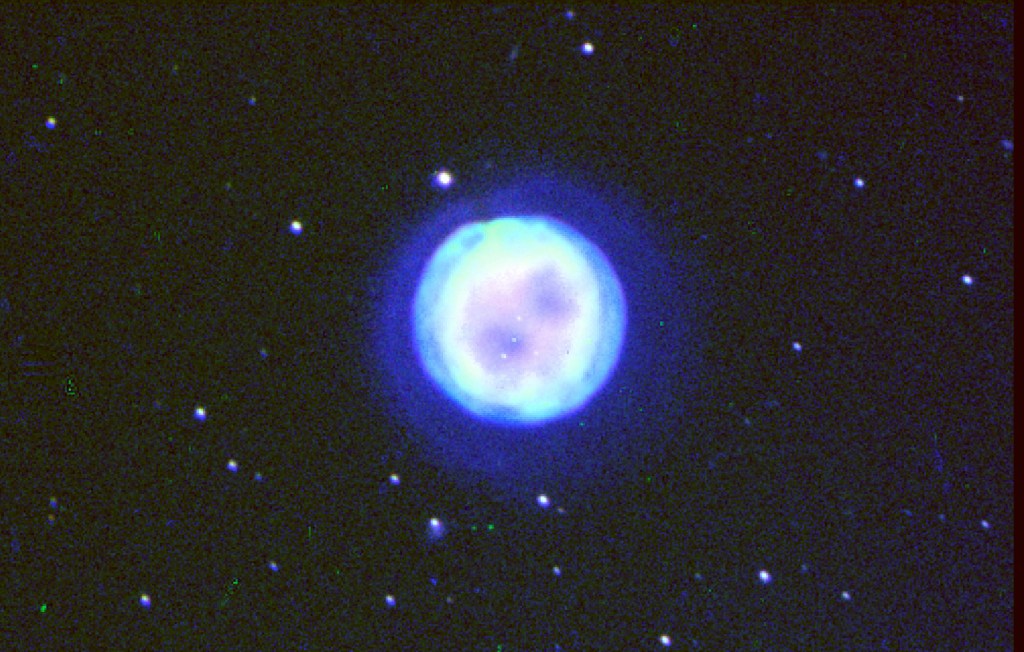
This one is slightly misleading, as one migh expect the entire owl including wings – but it is just its face. The Owl Nebula, scientifically cataloged as M97, is a planetary nebula located in the constellation Ursa Major. The term planetary nebula is just as misleading, as it has nothing to do with planets: This nebula is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from a dying red giant star.
4. Eagle Nebula (M16)
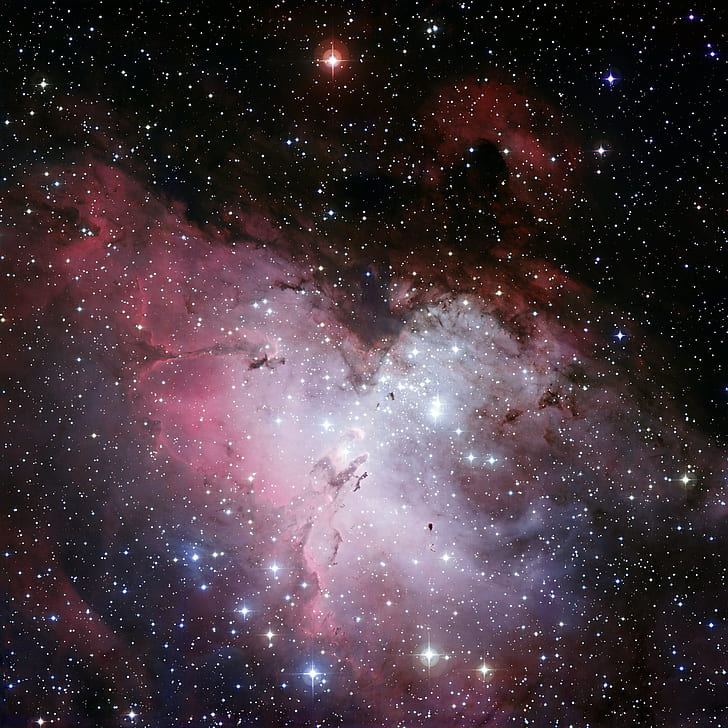

Now let’s visit the name-giving nebula of this entire homepage, the Eagle Nebula, also known as Messier 16 or the Star Queen Nebula. This a vast region of gas and dust situated in the constellation Serpens. You surely know it’s famous pillars of gas and dust, the Pillars of Creation. Within this stellar nursery, new stars are born amidst the turbulent clouds. The nebula looks like an eagle spreading its wings, and you can see the Pillars in the center of the image, slightly tilted to the left.
5. Seahorse Nebula (Barnard 150)
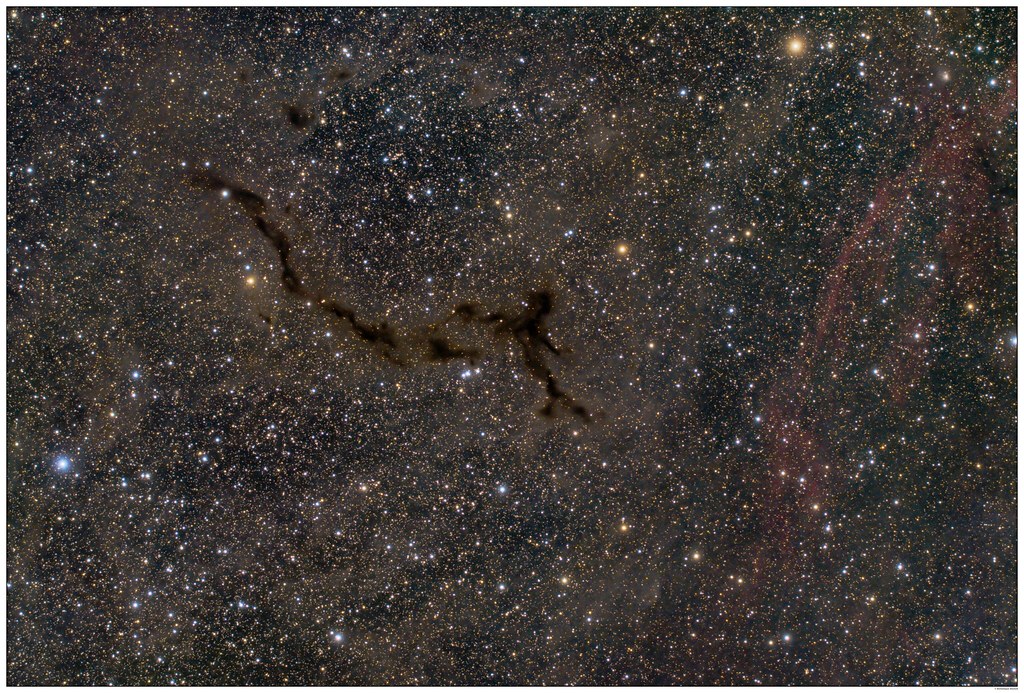

The Seahorse Nebula, cataloged as Barnard 150, is a vast region of ionized gas and young stars located in the constellation Cepheus (named after a king of Aethiopia in Greek mytholog)y. Its distinctive shape, reminiscent of a seahorse swimming through the cosmos, is formed by the interplay of stellar winds and radiation from massive stars within the nebula. Barnard 150 is a dark nebula or absorption nebula, which describes a dense cloud of interstellar dust that completely blocks out visible wavelengths of light from objects behind it, as NASA describes it.
6. Piggy Nebula (NGC 346)

NGC 346 is a young star cluster located in the Small Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. This stellar nursery is a hotbed of star formation. Its vibrant cluster of stars, illuminated by the energetic radiation emitted by its young, massive members, resembles a celestial jewel sparkling amidst the cosmic expanse. The original image does not look like a cute piggy, but when rotate, the shape clearly oinks out!
7. Horsehead Nebula (Barnard 33)
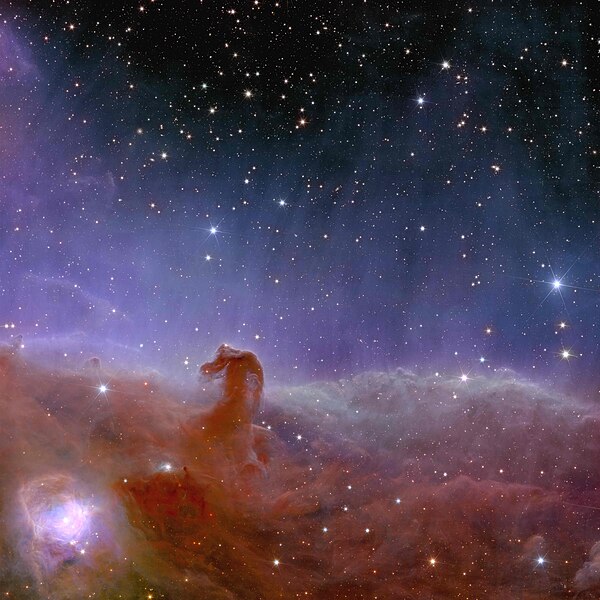

The Horsehead Nebula, designated as Barnard 33, is a dark nebula located in the constellation Orion. Its silhouette against the backdrop of glowing gas and dust in the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex gives it the appearance of a horse’s head, hence its name. Though shrouded in darkness, this iconic nebula serves as a stellar nursery, where the forces of gravity sculpt the birth of new stars.


Leave a comment